In the world of precision navigation, rtk gps (Real-Time Kinematic Global Positioning System) stands out as a game-changer. From autonomous vehicles to land surveying, RTK GPS has revolutionized how we measure location, offering centimeter-level accuracy that standard GPS simply can’t match. This article explores the science behind RTK GPS: a deep dive into accuracy, breaking down the technology, principles, and applications behind this innovation.
What is RTK GPS?
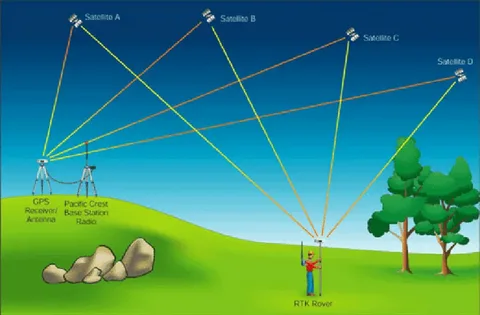
RTK GPS is an advanced positioning technique that enhances the accuracy of satellite-based positioning systems. Unlike traditional GPS, which typically provides accuracy within several meters, RTK GPS achieves accuracy within a few centimeters by correcting signal errors in real-time.
Key Components of RTK GPS
- Base Station: A stationary GPS receiver placed at a known location.
- Rover: A mobile GPS unit that receives corrections from the base station.
- Correction Data Link: Typically transmitted via radio, cellular networks, or the internet.
The base station compares its known location with the satellite signals it receives and calculates the error. It then sends this error information to the rover, which applies the correction and improves its positional accuracy.
How RTK GPS Achieves High Accuracy
To understand the science behind RTK GPS: a deep dive into accuracy, it’s essential to look at the underlying technology. RTK leverages carrier phase tracking, which measures the phase of the radio wave signal sent by GPS satellites rather than just the signal timing used in conventional GPS.
Carrier Phase Tracking
Standard GPS systems determine position by calculating the time it takes for signals to travel from satellites to the receiver. RTK goes a step further, using the phase of the satellite’s signal wave to achieve sub-centimeter precision.
Real-Time Error Correction
RTK works in real-time, constantly correcting for signal delays caused by the atmosphere, satellite orbit errors, and clock drift. These corrections are shared with the rover device nearly instantaneously, enabling accurate position fixes on the move.
Applications That Rely on RTK GPS
The incredible precision offered by RTK GPS has opened doors in many industries:
- Agriculture: For precision planting, spraying, and harvesting.
- Construction: In machine control and site layout.
- Surveying: For property boundary mapping and topographic surveys.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Ensuring precise vehicle positioning.
Each of these fields benefits from the ultra-high precision that RTK GPS provides, often eliminating the need for manual measurement and reducing errors drastically.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its high accuracy, RTK GPS isn’t without challenges:
- Line of Sight: Requires a clear signal path between satellites and receivers.
- Range Limits: Accuracy decreases as the distance from the base station increases.
- Environmental Interference: Signal blockages from buildings, trees, or terrain can reduce effectiveness.
Advanced solutions like Network RTK and multi-frequency receivers are helping to mitigate some of these issues, further enhancing the reliability of the technology.
Conclusion
The science behind RTK GPS: a deep dive into accuracy reveals a highly sophisticated system built on real-time corrections, carrier phase tracking, and precise error modeling. As industries continue to demand more precise location data, RTK GPS stands as a critical innovation in satellite navigation.
Whether you’re navigating a self-driving car or mapping a plot of land, understanding the science behind RTK GPS: a deep dive into accuracy helps appreciate the technology shaping our future.